Environment, Health, Safety and Sustainability
Building a healthier and more environmentally sustainable future
Environment, Health, Safety and Sustainability (EHS&S) refers to the practices to protect the health and safety of employees and the public as well as the environment. Strong EHS&S management requires the implementation of systems and processes to assess and control the risks of environmental impacts and health and safety hazards. Besides assuring compliance with applicable legislation, EHS&S management systems drive continuous improvement and learning.
Equally important, the rapidly growing rate of resource consumption throughout the world is unsustainable. The pharmaceutical industry recognizes that reversing the use of natural resources, the degradation of ecosystems and the disruption of the environmental systems that support human life, are critical for the benefit of current and future generations. Therefore, we believe that an increased focus on environmental sustainability is key for the future health of our planet.
EFPIA member companies strive to invent, produce and distribute new medicines and vaccines in a safe and environmentally responsible manner. Furthermore, we are actively providing a safe and healthy workplace while reducing the environmental impact in our operations and those of our supply partners around the world. A risk management approach is employed to create transformational health innovations, while protecting our employees and employing practical aspects of environmental sustainability.
Building a healthier and more environmentally sustainable futureEFPIA and its members recognise the urgent need to address climate change and safeguard natural resources, given the profound impact on both human health and nature. We further acknowledge concerns of pharmaceuticals in the environment. It’s essential to move away from traditional methods and adopt innovative practices that reduce our environmental impact. We strive to go beyond compliance on the targets set within the various EU legislative requirements as part of the EU Green Deal initiatives under the Zero Pollution, Circular Economy and Climate Action plans. As leaders in the pharmaceutical sector, we are committed to taking decisive actions to reduce our environmental impacts across the value chain and contribute to building resilient and sustainable health system. We are leading the transition towards the decarbonisation in the pharmaceutical sector by setting ambitious science- based targets, investing in renewable energy, driving circularity, and collaborating with stakeholders.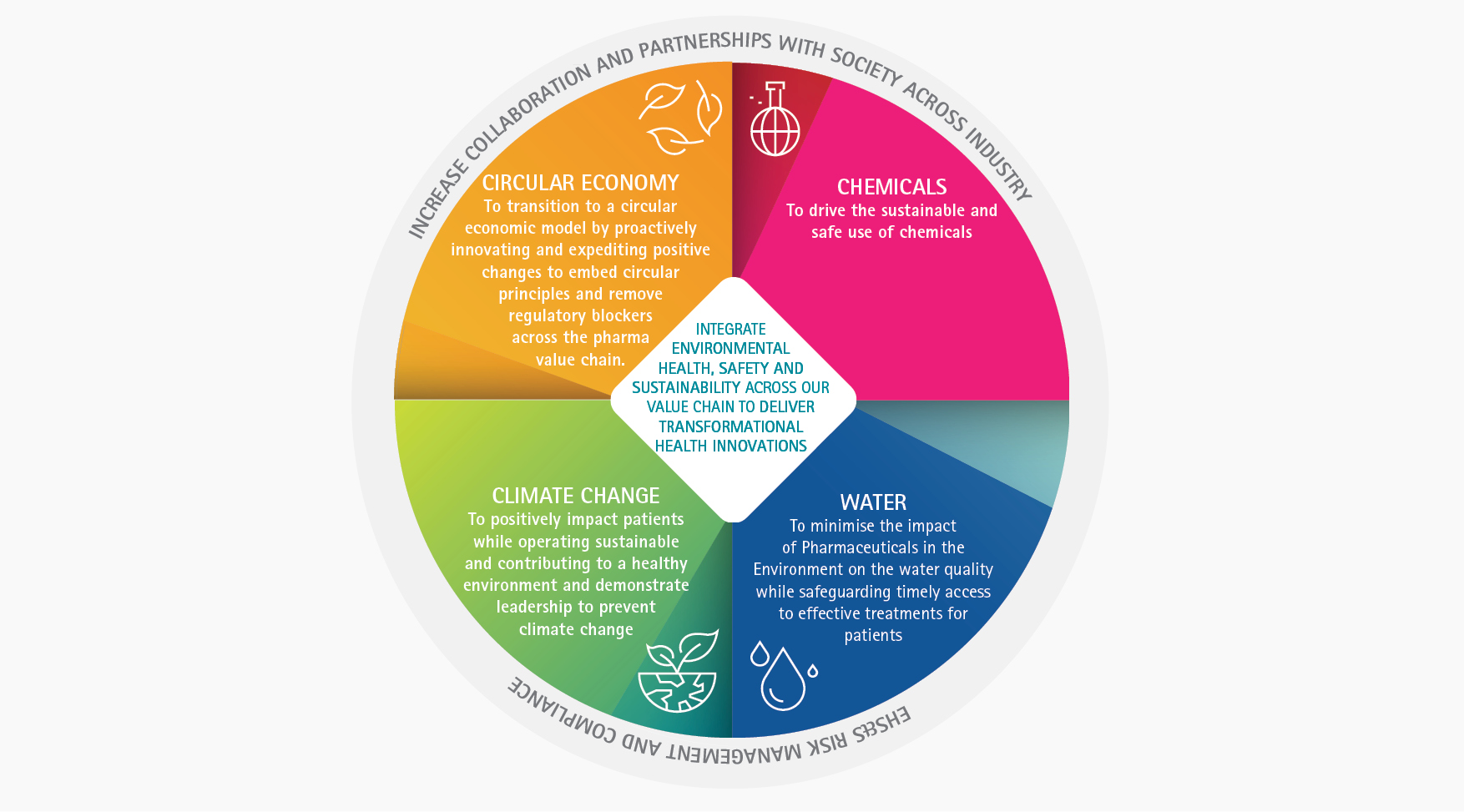
EFPIA welcomes and embraces the Commission’s focus on the Green Agenda and a more sustainable Europe, and looks forward to engaging constructively on the roll-out of their policy priorities.
Our members are dedicated to making a positive impact on the lives of patients whilst operating in a sustainable manner. As we have a responsibility toward the health of the population, we are moving forward in making a beneficial impact by actively addressing climate change and the transition to a circular economy with changes throughout the value chain, as we continue to innovate.

The European pharmaceutical industry is committed to continue playing an active role in addressing concerns around risks associated with Pharmaceuticals in the Environment (PiE). Minimising the impact of medicines on the environment while safeguarding access to effective treatments for patients is a critical issue across all sectors of healthcare.
At EFPIA, we believe that a collaborative approach allows us to increase our mutual knowledge and understanding on how to proactively address any potential risks imposed by the presence of PiE. To this end, EFPIA, AESGP and Medicines for Europe have developed the Eco-Pharmaco-Stewardship (EPS) framework that applies the widely accepted principles of product stewardship and is implemented across the industry and with broader stakeholders in the healthcare and environmental sector.
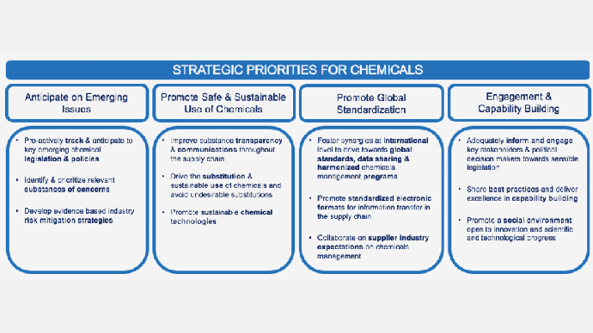
The pharmaceutical sector is one of the most regulated in Europe and the world. Accordingly, the pre-approval of manufacturing plants, clinical trials and marketing authorisations should be given consideration when implementing and interpreting some elements of EU Chemicals legislation. The long development timelines and highly regulated nature of this industry are fundamental aspects of the ability to react to changes in legislation (e.g. restriction of chemicals). Chemical processes comprise a significant portion of a medicine’s environmental footprint, and responsible use of chemicals is a key environmental stewardship priority for the sector.
Our member companies lead projects and initiatives to minimize the impact of their manufacturing process, including reducing the generation of hazardous waste, and using greener solvents. Due to the global operation of our companies and increasing number of countries with emerging chemical legislation, it is crucial that collaborations take place between industry and regulators globally.
EFPIA supports the need to develop a sustainable chemicals strategy and to promote research & development for the transformation of the chemical industry and the creation of green and sustainable manufacturing.
- NEW: Balancing challenges onEnvironment with access to medicines in Europe
- NEW - Interassociation paper on extended environmental risk assessment
- NEW - Responsible Manufacturing Effluent Management
- Interassociation Policy statement on responsible manufacturing effluent management
- Technical guidance document on responsible manufacturing effluent management
- Slide set on the guidance, including real world examples
- Eco-Pharmaco-Stewardship (EPS) initiative – Care for people & our environment
- Joint statement on the European Parliament’s Resolution and on the Strategic Approach to PiE
- Joint Statement on the EU Strategic Approach to PiE
- Industry contribution to a Strategic Approach to PiE – guest blog
- Joint declaration on Pharmaceuticals in the Environment
- EU Strategic Approach to PiE (EU Commission)
- EU Parliament Resolution on a Strategic Approach to PiE
- iPiE IMI Project
- Q&A on pharmaceuticals in the environment
- Titanium dioxide and alternatives - Industry submission to EMA Feb 2024
- NEW: PFAS infographic
- NEW: EFPIA Report In Response The Annex XV PFAS Restriction Proposal
- NEW: Annex 1 Socio-Economic Analysis Of the potential restriction of PFAS used in the production, packaging and delivery of human medicinal products
- NEW: Annex 2 Impact of Proposed PFAS Restriction on Patient Access to Medicines & EU Strategic Autonomy
- NEW: Annex 3 Use of Fluoropolymers and Fluoro-Elastomers in Medicinal Product Manufacturing Facilities
- NEW - Report on current and proposed CLP hazard classes
- EFPIA and AnimalHealthEurope's Position on PFAS
- Integration of the Essential Use Concept into REACH
- EFPIA Substance Regulatory Compliance Declaration for Articles
- Industry Pioneers the Contribution of Substance Data to decrease animal testing
- EFPIA response to Commission roadmap on chemicals strategy for sustainability 2020
- EFPIA Paper on Material Declaration
- EFPIA position on microplastics 2019
- Commission roadmap on chemicals strategy for sustainability
- Commission webpage microplastics
Climate change
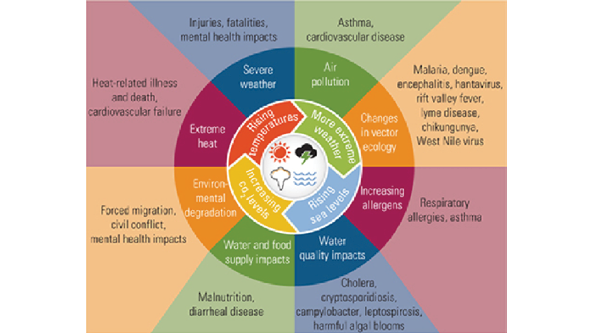
Direct or indirect human activities have altered the composition of the global atmosphere and increased carbon dioxide emissions, driving up temperatures. This has led to what we often observe as more extreme weather conditions and is referred to as climate change.
- Establish and further develop climate policies based on materiality and impact for individual companies, whilst addressing their entire value chains
- Annually and publicly disclose progress towards co2 e reduction targets using recognised methodologies, and verified by third parties
- Increase the share of renewable energy at their facilities and along the global value chains
- Set science-based CO2 reduction targets
- Contribute to reduced energy consumption and increased energy efficiency
Circular economy

The Pharmaceutical Industry is supportive of a circular approach to its operations and products and is aligned with the European Commission's Circular Economy Action Plan. We will achieve the goals of the Circular Economy Action Plan concurrent with our aspiration to safeguard the future supply of pharmaceuticals for patients and improve human health.
The pharmaceutical industry’s approach to circularity builds on our long experience in environmental sustainability, while recognizing the constraints (e.g. speed of transition), from operating in a highly regulated industry. Circularity and regulation of pharmaceuticals should be carefully balanced. The innovation to enable circularity will drive new opportunities for growth, promote greater resource efficiency, create a more competitive economy and reduce pollutants.
Implementation of a circular economy is fundamental to help limit the global temperature increase to less than or equal to 1.5C, and we welcome the opportunity to be part of the solution by working collaboratively with the EU in shaping the legislative framework and within our organizations to mitigate our impacts.
IMI projects



- identify potential hazards associated with APIs in development and explore the options to steer the design process in a greener direction;
- make relevant environmental data on APIs more visible and accessible to all stakeholders.
Initiatives & Alliances
#medsdisposal is a campaign to raise awareness on how to dispose of unused or expired medicines appropriately in Europe, bringing information on current disposal schemes in European countries to one place. It is a joint initiative between European healthcare, industry and student organisations;

The Pharmaceutical Supply Chain Initiative (PSCI) is a group of pharmaceutical and healthcare companies who share a vision of better social, health, safety and environmental outcomes in the communities where they buy. Collectively PSCI members can share knowledge and expertise, across the industry, to drive complex, global change more effectively than any one organisation alone. The companies have joined forces to promote responsible supply chain management and better business conditions across the industry.

Antimicrobial resistance poses a formidable threat to the attainment of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The United Nations called in 2016 for concerted action from governments and various sectors to address the implications of antimicrobial resistance in a comprehensive manner, and implement strategies at national level. The AMR Industry Alliance , led by the IFPMA, was the life-sciences industry response to the call for action.
The Alliance supports the increasing recognition that the value assigned to antibiotics and diagnostics often does not reflect the benefits they bring to society, nor the investment required for their creation.
The signatory companies committed to work to reduce the development of microbial resistance; invest in R&D that meets global public health needs with new innovative diagnostics and treatments; and to improve access to high-quality antibiotics and ensuring that new ones are available to all.
Read more

A sustainable pharmacy chain will only be successfully realised by means of extensive collaboration between the parties that form the chain itself, from the development and acceptance of medicines, through distribution, prescription and use, to waste processing and water purification. In signing the Green Deal for Sustainable Care, the Sustainable Pharmacy Coalition is committed to improving sustainability and is focusing on the following three cornerstones: encouraging circular working methods, clean water/combating medicine residues in water, and reducing CO2 emissions. See the summary of underlying goals.
Link to report